Quickstart¶
This page is a brisk instruction to using fahr.
First install fahr, if you haven’t done so already:
$ pip install fahr[kaggle]
For the purposes of this demo we will use a very simple train.py which builds a tiny keras feedforward neural network on synthetic data. This script uses numpy and keras so we’ll need to install these packages also:
$ yes | pip install numpy keras
$ curl https://gist.githubusercontent.com/ResidentMario/ab3ce65a9bd5bc4061237a374fd9e67a/raw/train.py -o train.py
fahr takes a training artifact such as this one as input. Training artifacts may be either .py Python scripts or .ipynb Jupyter notebooks, and they must write serialized model assets to disk upon completion.
Assuming you have access to the Kaggle API (see here for details) you can now submit your training job in just one line of code (in all of the lines of code that follow, replace my Kaggle username, ResidentMario, with your own):
$ fahr fit 'train.py' --train-driver='kaggle' --config.username='ResidentMario'
fahr.fahr - INFO - Writing kernel metadata to "kernel-metadata.json".
fahr.fahr - INFO - Fitting ResidentMario/train training job.
fahr.fahr - INFO - The training job is now running. To track training progress visit https://www.kaggle.com/ResidentMario/train. To download finished model artifacts run fahr fetch --driver="kaggle" ./ "ResidentMario/train" after training is complete.
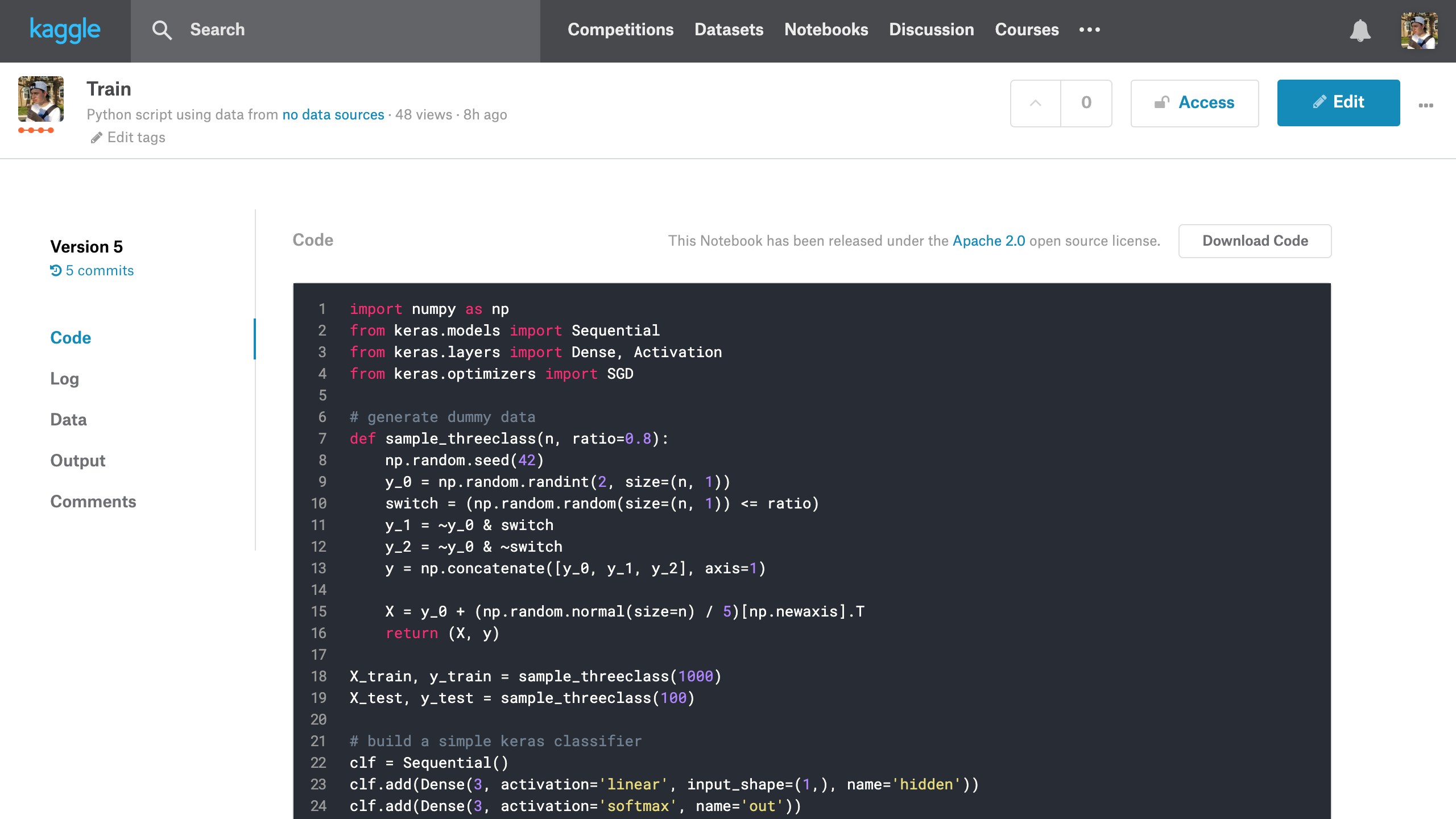
You can visit the web interface to your training job by clicking on the kernel link. Here’s mine:
Once the job has completed running, you can go ahead and download a model artifact using the command documented in the log output. This will download model.h5 to your local machine:
$ fahr fetch --train-driver="kaggle" ./ "$USERNAME/train"
fahr.fahr - INFO - Downloaded model artifact(s) to ".".
$ ls
$ model.h5 train.py Dockerfile run.sh
And that’s it, you’re done!
Every training driver in fahr has just two steps: running fit to turn a training artifact into a model artifact “on the cloud”, and then running fetch to download the result to local disk.
To learn more about the fahr workflow, see the User Guide.